What network services does AWS provide?
AWS offers a pretty rich set of networking services that cover connectivity, traffic management, security, and hybrid/cloud-to-cloud setups.
Let’s start with the basics first.
IP Addresses
IPv4
IPv4 is the standard 32-bit address system to identify resources on a network.
Note: All public IPv4 addresses (incl. Elastic IPs) are billed at $0.005/hr.
Public IPv4
Used to access resources via the internet.
Note: EC2 instances get a new public IPv4 address on stop/start.
Private IPv4
Used within VPCs for internal communication
Note: Remains the same after instance restart.
Elastic IP
Fixed public IPv4 attached to an EC2.
Useful for stable endpoints (e.g. VPNs).
IPv6
IPv6 is a 128-bit addressing system where all addresses are public.
Note: IPv6 is free to use in AWS.
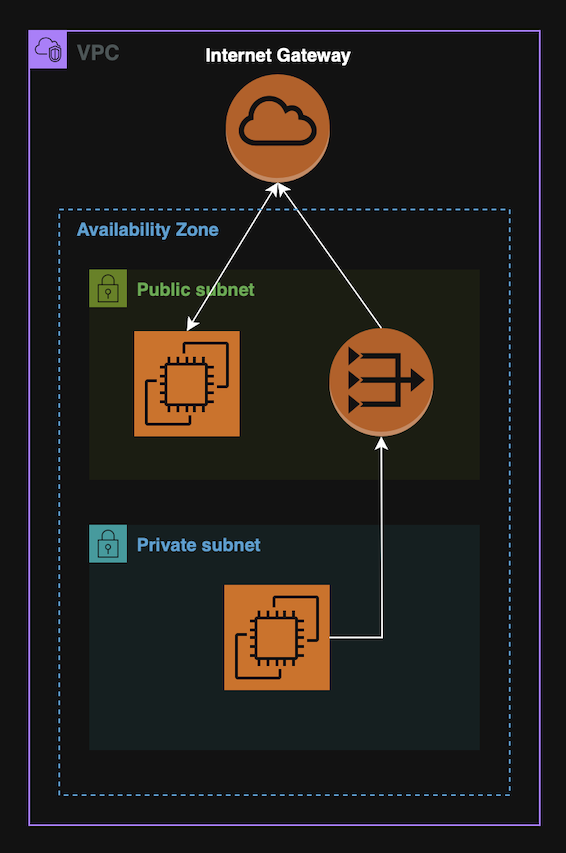
VPCs
A Virtual Private Network, (VPC), is an isolated AWS network where it is possible to deploy resources.
VPCs usually contain subnets. A subnet is a range if IPs inside a VPC, associated with a specific AZs.
Subnets can be:
- Public - Has route to internet Gateway;
- Private - No direct internet access. Needs NAT (Gateway or Instance).
VPC Flow Logs
VPC Flow Logs capture network traffic logs from VPC components.
Note: Can monitor traffic at different levels, (VPC, Subnet, ENI).
Use cases: Troubleshooting, auditing and monitoring.
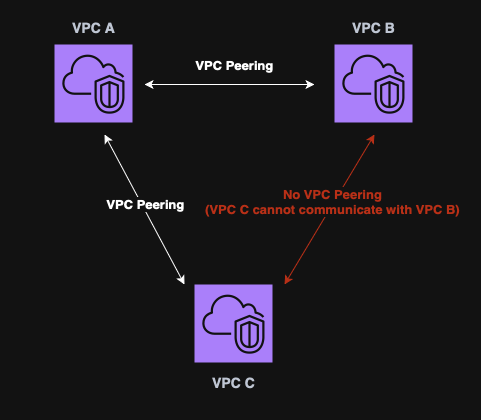
VPC Peering
VPC Peering is used to connect two VPCs privately over AWS’s network.
Key points:
- No CIDR overlapping is allowed;
- Can connecct VPCs from different regions;
- Not transitive. (VPC A ←> VPC B and VPC B ←> VPC C, does not mean that VPC A ←> VPC C).
VPC Endpoints
A VPC Endpoint provides private access to AWS services without using the internet.
VPC Endpoints improve security & latency and eliminate the need for Internet Gateways or NAT.
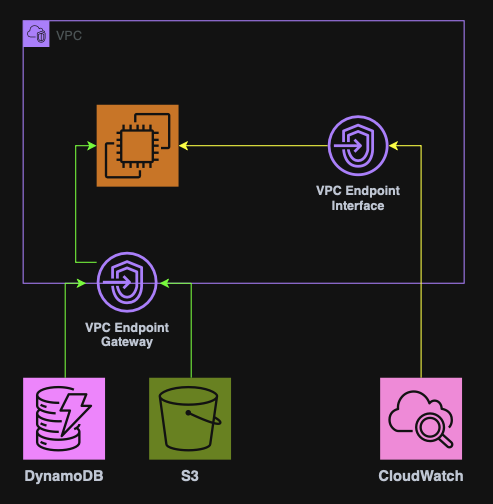
There are two types of VPC Endpoints:
Gateway Endpoint
Interface Endpoint
Used by all other services.
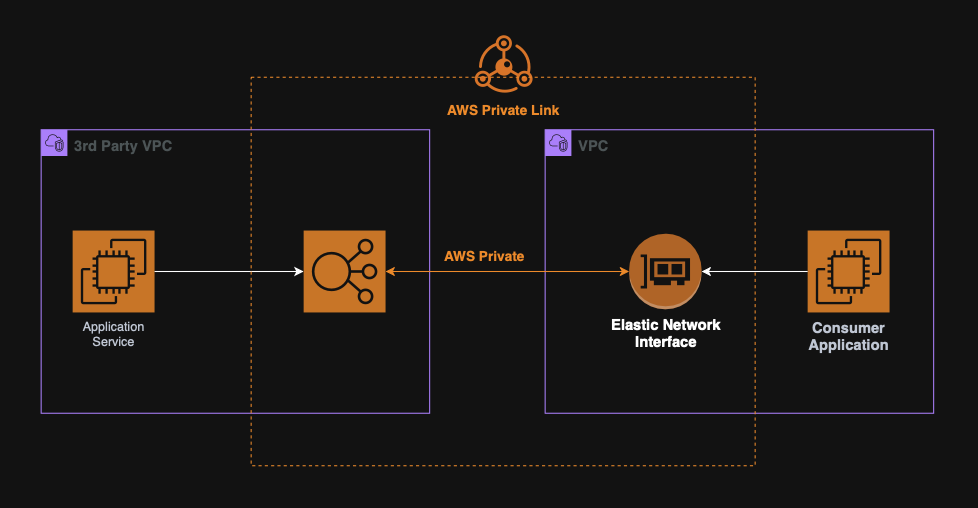
PrivateLink
PrivateLink is used to privately expose services hosted in one VPC to another VPC.
This is a more scalable and secure option that VPC Peering and great for SaaS applications or internal micro-services.
Site-to-Site VPN & Direct Connect
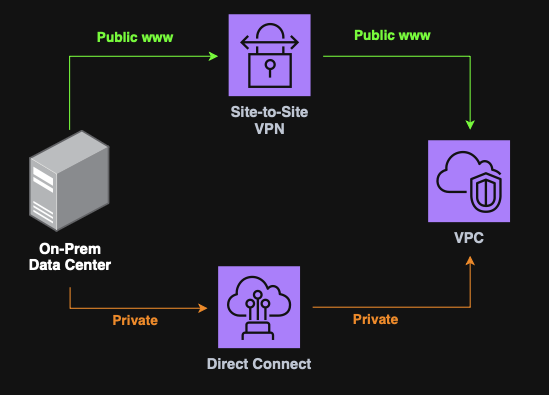
Site-to-Site VPN
Site-to-Site VPN is an encrypted connection between an on-prem Data Center and an AWS VPC over the public internet.
It required a Customer Gateway (on-prem) and a Virtual Private Gateway (AWS).
Note: May raise some latency and security considerations despite encryption.
Direct Connect (DX)
Direct Connect is a private, dedicated physical connection between on-prem and AWS
Note: DX bypasses the public internet, (faster & more secure), however, it takes ~1 month to provision.
AWS Client VPN
The AWS Client VPN securely connects user devices, (laptops, etc.) to a VPC.
It works over the public internet and scales up to thousands of users.
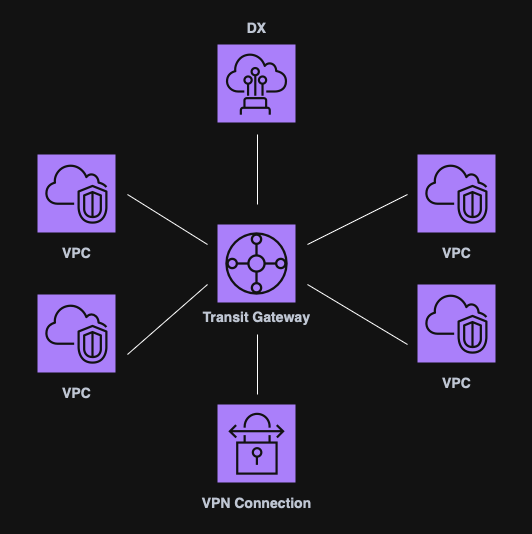
Transit Gateway (TGW)
A Transit Gateway is a centralized hub used to connect multiple VPCs and VPNs.
Key points:
- Scales better that point-to-point peering;
- Non-transitive peering replaced by a single TGW route table;
- Does not use the public internet for routing.
NACL & Security Groups
NACL (Network ACL)
NACL is a stateless firewall at the subnet level.
It allows for ALLOW and DENY IP based rules that are evaluated in order.
Security Groups
A Security Group is a stateful firewall attached to an EC2 or ENIs, (Elastic Network Interfaces).
It is applied at the instance level and only ALLOW rules can be defined.